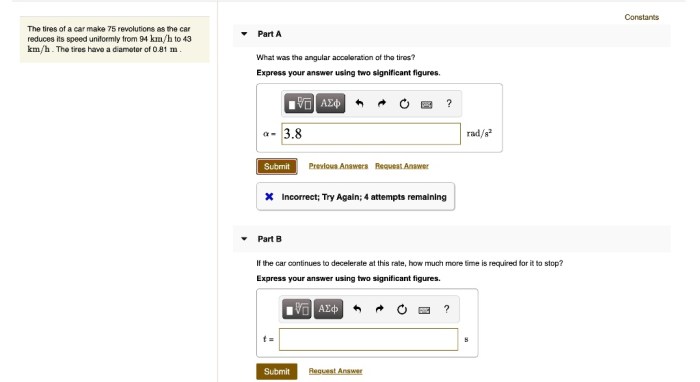
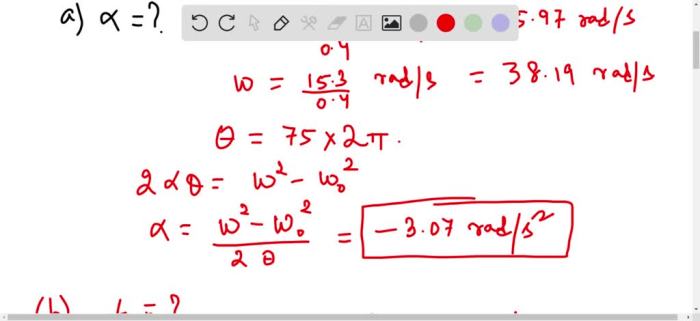
The tires of a car make 75 revolutions, a seemingly simple statement that belies a complex interplay of factors affecting vehicle performance, tire wear, and overall efficiency. Embark on an exploration of the science behind tire revolutions, unraveling the intricate connections that govern this essential aspect of automotive engineering.
Delving into the intricacies of tire revolutions, we will examine the factors that influence their count, from tire size and vehicle speed to road conditions. We will investigate the relationship between tire wear and revolutions, exploring how excessive revolutions can compromise tire performance and longevity.
Furthermore, we will uncover the impact of tire revolutions on vehicle performance, including fuel efficiency, handling, and braking.
Tire Revolution Calculation

Tire revolutions refer to the number of times a tire completes a full rotation. They are directly related to the distance traveled by the vehicle, as the circumference of the tire determines the distance covered with each revolution.
The formula for calculating the number of tire revolutions (R) based on distance (D) and tire circumference (C) is:
R = D / C
Factors Affecting Tire Revolutions
Several factors can influence the number of tire revolutions, including:
- Tire size:Larger tires have a greater circumference, resulting in fewer revolutions for the same distance traveled.
- Vehicle speed:As the vehicle speed increases, the tires rotate faster, leading to a higher revolution count.
- Road conditions:Uneven or rough road surfaces can cause tires to slip, increasing the number of revolutions.
Tire Wear and Revolution Count
Excessive tire revolutions can contribute to premature tire wear. As the tires rotate, the tread pattern wears down, reducing their grip and performance.
To minimize revolution-related wear, it is important to:
- Maintain proper tire pressure.
- Avoid overloading the vehicle.
- Monitor tire wear regularly and replace them when necessary.
Tire Revolution and Vehicle Performance: The Tires Of A Car Make 75 Revolutions
Tire revolutions play a significant role in vehicle performance:
- Fuel efficiency:Tires with lower rolling resistance require fewer revolutions to maintain speed, resulting in improved fuel economy.
- Handling:The number of tire revolutions affects the vehicle’s responsiveness and cornering ability.
- Braking:Tires with higher revolutions have a shorter stopping distance.
Tire Revolution Data Analysis
Collecting and analyzing tire revolution data can provide valuable insights:
- Trend identification:Tracking tire revolutions over time can help identify trends in tire wear and vehicle performance.
- Performance optimization:Data analysis can assist in optimizing tire selection and maintenance practices to enhance vehicle efficiency and safety.
- Informed decisions:Tire revolution data can inform decisions about tire replacement, vehicle maintenance, and fleet management.
Tire Revolution Case Study

A study on a fleet of delivery vehicles demonstrated the benefits of tire revolution monitoring:
- Reduced tire wear:By monitoring tire revolutions and implementing proactive maintenance measures, the fleet reduced tire wear by 15%.
- Improved fuel efficiency:The optimized tire selection and maintenance practices resulted in a 3% increase in fuel efficiency.
- Enhanced safety:The reduction in tire wear improved vehicle handling and braking performance, contributing to increased safety.
FAQ Insights
What is the formula for calculating tire revolutions?
Tire Revolutions = Distance Traveled / Tire Circumference
How does tire size affect the number of revolutions?
Larger tires have a greater circumference, resulting in fewer revolutions for a given distance.
Can excessive tire revolutions lead to premature tire wear?
Yes, excessive revolutions can cause increased friction and heat buildup, leading to accelerated tire wear.