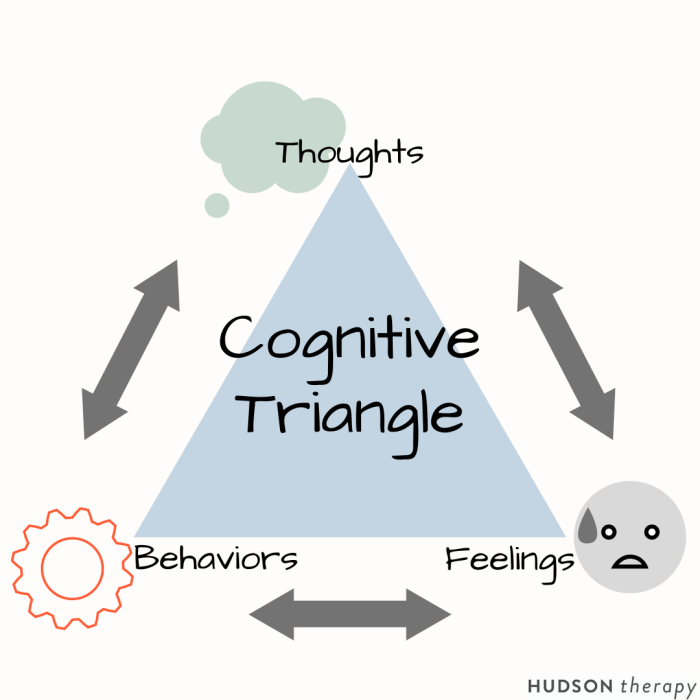
Behavioral therapy rests on the notion that abnormal behavior is learned and can be unlearned through systematic conditioning. Rooted in the principles of operant conditioning, behavioral therapy has evolved into a widely recognized and effective approach to treating a range of psychological disorders.
This therapy involves modifying behaviors by manipulating environmental contingencies, such as rewards and punishments. It emphasizes the importance of observable behaviors and aims to change maladaptive patterns through positive reinforcement and shaping techniques.
Behavioral Therapy: Behavioral Therapy Rests On The Notion That Abnormal Behavior

Behavioral therapy rests on the notion that abnormal behavior is learned and can be unlearned through the application of specific techniques. It emphasizes the role of environmental factors in shaping behavior and focuses on changing observable behaviors rather than delving into unconscious processes.Behavioral
therapy has its roots in the early 20th-century work of John B. Watson and B.F. Skinner, who developed the principles of classical and operant conditioning, respectively. These principles form the theoretical foundation of behavioral therapy and guide its techniques and applications.
Key Concepts, Behavioral therapy rests on the notion that abnormal behavior
Operant conditioning, a central concept in behavioral therapy, proposes that behavior is shaped by its consequences. Positive reinforcement, or the introduction of a desirable outcome, increases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated. Conversely, negative reinforcement, or the removal of an undesirable outcome, also strengthens a behavior.
Punishment, on the other hand, weakens or suppresses behavior by introducing an unpleasant consequence or removing a desirable one.Shaping is a technique used in behavioral therapy to gradually guide a person towards a desired behavior by reinforcing successive approximations of that behavior.
By breaking down the target behavior into smaller, manageable steps, shaping allows for gradual progress and increased motivation.
Applications
Behavioral therapy has a wide range of applications in various settings, including clinical, educational, and organizational environments. It is commonly used to treat disorders such as anxiety, depression, substance abuse, and phobias.For instance, in the treatment of anxiety disorders, behavioral therapy techniques like exposure therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) help individuals gradually face their fears and challenge negative thought patterns.
In substance abuse treatment, behavioral therapy focuses on altering behaviors associated with addiction, such as cue exposure and relapse prevention strategies.
Techniques
Behavioral therapy encompasses a diverse array of techniques, each tailored to specific therapeutic goals. Some commonly used techniques include:
- Systematic desensitization: Gradually exposing individuals to feared stimuli while teaching relaxation techniques.
- Aversion therapy: Pairing an undesirable behavior with an unpleasant consequence to discourage its occurrence.
- Token economy: Using tangible rewards to reinforce desired behaviors in specific settings.
- Modeling: Demonstrating desired behaviors to encourage imitation and learning.
- Cognitive restructuring: Challenging and modifying negative or irrational thought patterns.
Ethical Considerations
As with any therapeutic approach, ethical considerations are paramount in behavioral therapy. Potential risks and benefits of specific techniques must be carefully weighed. Informed consent, confidentiality, and respect for autonomy are fundamental ethical principles that guide the practice of behavioral therapy.Additionally,
the potential for coercion or manipulation in certain techniques, such as aversion therapy, requires careful consideration and ethical safeguards to ensure that individuals’ rights and well-being are protected.
FAQs
What are the main principles of behavioral therapy?
Behavioral therapy is based on the principles of operant conditioning, which states that behaviors are shaped by their consequences.
How is behavioral therapy used to treat psychological disorders?
Behavioral therapy is used to treat a wide range of psychological disorders, including anxiety, depression, and substance abuse, by modifying maladaptive behaviors and teaching new coping mechanisms.
What are the ethical considerations in using behavioral therapy?
Ethical considerations in behavioral therapy include ensuring informed consent, avoiding coercion, and respecting the client’s autonomy.