Identify the predominant intermolecular force – Embarking on a scientific expedition, we delve into the fascinating realm of intermolecular forces, the unseen yet potent interactions that govern the behavior of matter. At the forefront of our inquiry lies the crucial task of identifying the predominant intermolecular force, a defining characteristic that unveils the secrets of a substance’s physical properties and chemical reactivity.
Through a systematic approach, we unravel the complexities of intermolecular forces, exploring their diverse types and the factors that influence their strength. Armed with this knowledge, we establish a roadmap for discerning the predominant intermolecular force, empowering us to decipher the molecular architecture of substances and predict their behavior.
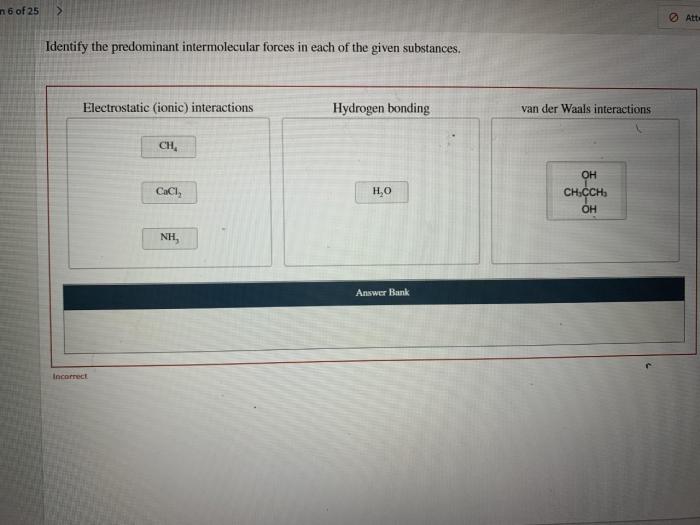
1. Intermolecular Forces: Identify The Predominant Intermolecular Force
Intermolecular forces are attractive or repulsive forces that act between molecules. They are weaker than the intramolecular forces that hold atoms together within a molecule.
There are three main types of intermolecular forces:
- Dipole-dipole forcesoccur between molecules that have a permanent dipole moment. This means that the molecule has a positive end and a negative end.
- London dispersion forcesoccur between all molecules, even those that do not have a permanent dipole moment. These forces are caused by the temporary fluctuations in the electron distribution of a molecule.
- Hydrogen bondingis a special type of dipole-dipole force that occurs between molecules that have a hydrogen atom bonded to a small, electronegative atom such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine.
The strength of intermolecular forces depends on several factors, including the size and shape of the molecule, the polarity of the molecule, and the temperature.
2. Identifying Predominant Intermolecular Force
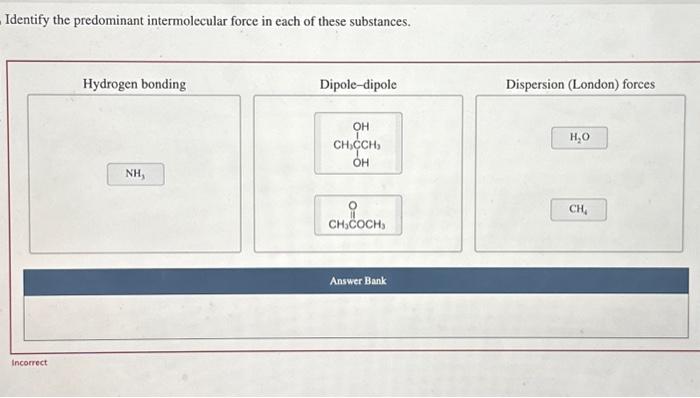
To identify the predominant intermolecular force of a substance, you need to consider the following factors:
- The physical state of the substance at room temperature
- The boiling point of the substance
- The solubility of the substance in water
The following table summarizes the characteristics and examples of substances with different predominant intermolecular forces:
| Predominant Intermolecular Force | Physical State at Room Temperature | Boiling Point | Solubility in Water | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dipole-dipole forces | Liquid | Moderate | Partially soluble | Ethanol, acetone |
| London dispersion forces | Gas | Low | Insoluble | Methane, ethane |
| Hydrogen bonding | Liquid or solid | High | Very soluble | Water, ammonia |
3. Applications of Intermolecular Forces
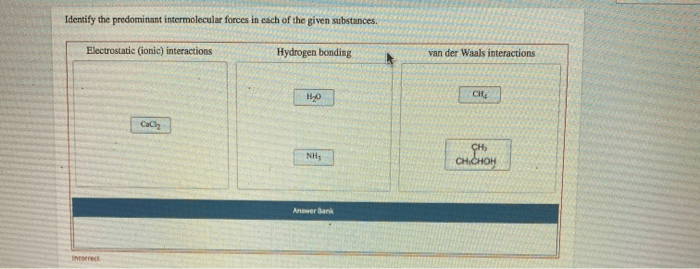
Intermolecular forces play a major role in determining the physical properties of substances. For example, the boiling point of a substance is determined by the strength of the intermolecular forces between its molecules. Substances with strong intermolecular forces have higher boiling points than substances with weak intermolecular forces.
Intermolecular forces are also used in a variety of applications, such as:
- Adhesionis the force that holds two different substances together. It is caused by the intermolecular forces between the molecules of the two substances.
- Cohesionis the force that holds molecules of the same substance together. It is caused by the intermolecular forces between the molecules of the substance.
- Capillary actionis the ability of a liquid to rise in a narrow tube. It is caused by the intermolecular forces between the liquid molecules and the molecules of the tube.
4. Advanced Concepts
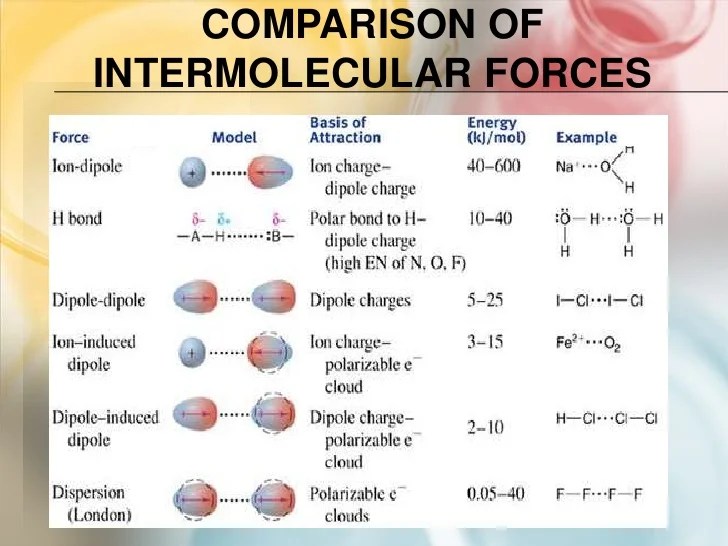
In addition to the three main types of intermolecular forces discussed above, there are also several other types of intermolecular forces that can be important in certain situations. These include:
- Ion-dipole forcesoccur between ions and polar molecules.
- Ion-induced dipole forcesoccur between ions and nonpolar molecules.
- Pi-pi interactionsoccur between molecules that have pi bonds.
Intermolecular forces also play an important role in molecular recognition and self-assembly. Molecular recognition is the ability of molecules to recognize and bind to each other. Self-assembly is the ability of molecules to spontaneously organize themselves into larger structures.
Intermolecular forces are studied using a variety of experimental techniques, including:
- Infrared spectroscopy
- Raman spectroscopy
- X-ray crystallography
- Neutron scattering
FAQ Section
What is the significance of identifying the predominant intermolecular force?
Identifying the predominant intermolecular force provides insights into a substance’s physical properties, chemical reactivity, and behavior under various conditions.
How does the strength of intermolecular forces affect a substance’s properties?
The strength of intermolecular forces determines a substance’s melting point, boiling point, viscosity, and other physical properties.
What are the different types of intermolecular forces?
The main types of intermolecular forces include dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces.